In the medical field, ensuring that all equipment is properly sterilized is crucial to preventing infections and maintaining patient safety. Whether it’s surgical instruments, diagnostic tools, or even electronic devices, proper sterilization techniques must be followed to eliminate harmful pathogens.
Types of Sterilization Methods
There are several methods available for sterilizing medical equipment, each with its own advantages and considerations:
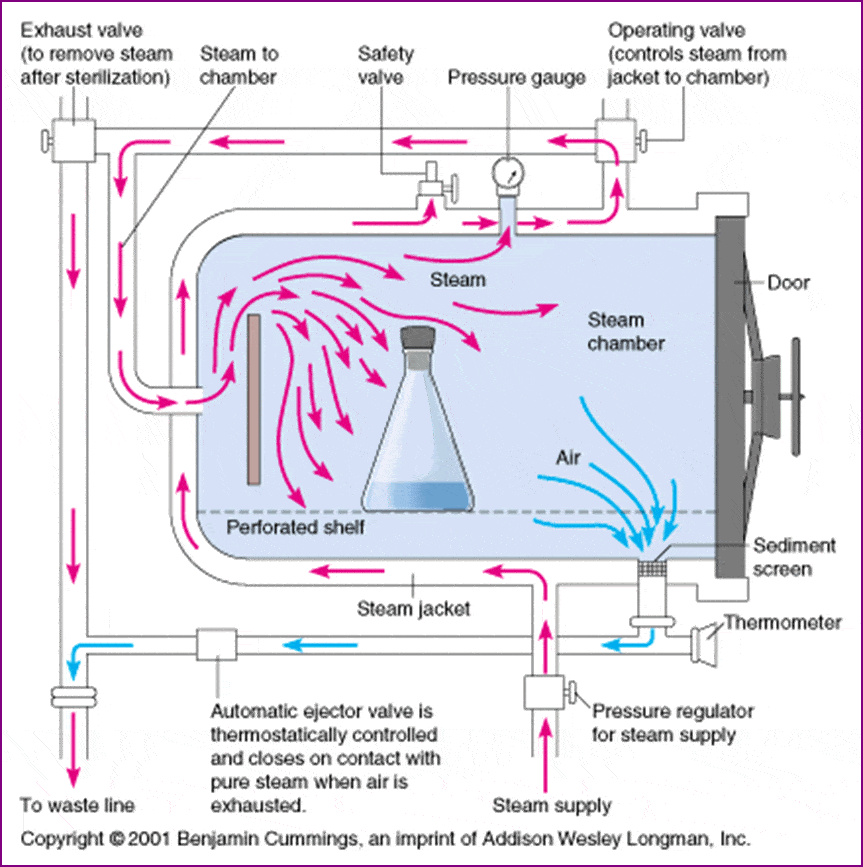
Autoclaving: This is one of the most common methods of sterilization, using high-pressure steam to kill bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Chemical Sterilization: Chemical agents such as ethylene oxide or hydrogen peroxide can be used to sterilize equipment that is heat-sensitive.
Radiation Sterilization: Gamma rays or electron beams can be used to sterilize equipment that cannot withstand heat or chemicals.
Gas Sterilization: Gaseous agents like ozone or chlorine dioxide can be used to sterilize equipment in a sealed chamber.
Best Practices for Sterilization
Regardless of the method used, there are some universal best practices that should be followed when sterilizing medical equipment:
Thorough Cleaning: Before sterilization, all equipment should be cleaned to remove any debris or organic material that could interfere with the sterilization process.
Proper Packaging: Equipment should be properly packaged to protect it during sterilization and storage, and to prevent recontamination.
Validation: Sterilization processes should be validated to ensure they are effective at killing pathogens without causing damage to the equipment.
Monitoring: Regular monitoring of sterilization processes should be conducted to ensure they are consistently effective.
Training: Staff responsible for sterilizing medical equipment should be properly trained in the correct techniques and procedures.
Challenges in Sterilizing Medical Equipment
While proper sterilization is critical, there are challenges that can arise in the process:
Complex Equipment: Some medical equipment is intricate and difficult to sterilize effectively, requiring special attention to detail.
Human Error: Mistakes in the sterilization process can occur due to human error, underscoring the importance of thorough training.
Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare facilities must comply with strict regulations regarding the sterilization of medical equipment to ensure patient safety.
Conclusion
Ensuring that medical equipment is properly sterilized is essential for maintaining a safe and hygienic healthcare environment. By following best practices and staying informed about the latest sterilization techniques, healthcare providers can protect both patients and staff from the risk of infections.